Just a quick note about Cincinnati Bell FiOptics Gigabit service, it’s pretty much fantastic. I ran this tonight (2014-10-06 23:16:45 EDT), and although I’ve had the download a bit faster (as much as 850 Mbps), this is still amazingly fast internet.
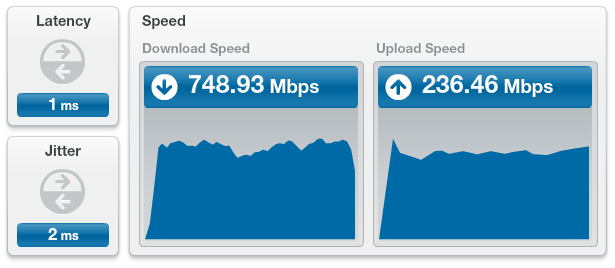
But one thing I think that’s worth mentioning, and something Cincinnati Bell does at least a decent job of doing themselves, is that you will not be able to achieve these speeds without hardware to support gigabit internet. Without actually looking it up, I would guess that most Macs built within the past 5 years (or so) have a gigabit Ethernet port. More recent PCs probably have this as well. But what will really trip you up is your network hardware. In my household we have a number of Apple Airport Extreme’s which have gigabit ports, both on the LAN and WAN ports. What I discovered, however, is that converting a WAN input (from the FiOptics 1 Gbps service) to a useable 1 Gbps LAN output is not as simple as making sure the WAN and LAN ports are the gigabit variety. The best my Apple hardware could muster is about 250 Mbps. I ended up referencing the following WAN to LAN chart in order to find a router capable of converting WAN to LAN at the full 1 Gbps. As you can see via my results above, accounting for overhead and some network congestion, I’m pulling (more or less) the 1000 / 250 Mbps connection I was told I could receive. I say “could” because they only guarantee 300 Mbps down … I’m not sure what an acceptable upload speed is.
In summary, the speed is fantastic.
2014-10-07 Update
I found a Speedtest.net server in Chicago (Comcast, ironically) that would allow me to test at 1 Gbps.

2015-04-07 Update
Speeds are as good, if not better, 6 months later. I see fiber lines going up (or already up) all over the city. If you can get FiOptics Gigabit service, I highly recommend it!
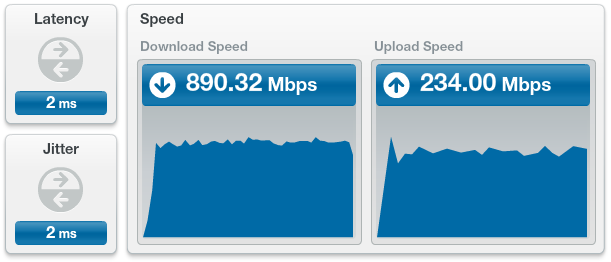
2015-10-27 Update
While Speedtest.net speeds are still good, depending on the server you hit, you never see these speeds in real-world usage. Even big companies like Apple or Microsoft that use CDNs don’t allow (or cannot provide due to capacity constraints) much more than 100 – 150 Mbps. That said, most places will let you upload at almost full speed (~ 200 Mbps), which when compared to typical upload speeds of < 10 Mbps almost makes it worth it.

2016-03-05 Update
Download and upload speeds still seem to be just as high as ever, though as noted before, one rarely sees these kinds of speeds unless downloading from multiple sources at once. During peak hours, I may still be able to pull over 500+ Mbps on a bandwidth test but have Netflix or iTunes on the Apple TV essentially have to buffer the content before I can view it.
Something I’m interested to see pan out is comparing my 1000 / 250 Mbps service at home with my 100 / 50 Mbps service at the office. So far I haven’t been able to tell a big difference between the two speeds, but it is noticeable, especially when OS X or iOS updates are released and all the devices in the office are updating at once and the office connection becomes saturated.

2016-07-14 Update
More of the same, which is certainly good news!

2016-12-28 Update
No matter how when I try, I don’t seem to be able to pull anything close the the above speeds using speedtest.net. Even from Cincinnati Bell’s own speedtest page, I get about 550 / 200 Mbps and no more. I just so happened to wander over to DSLReports and ran their speedtest and was happier with those results. I’ll likely continue to use them instead of anything else, though I feel like I’m fishing for a speedtest that shows me what I want to see. Anyway, here is what I was able to get tonight:

The C rating for Top Speed is based on my own value of 1000 Mbps, though clearly I wasn’t, nor ever will, get anything near that speed in real-world scenarios.
2017-07-09 Update
Per my last update, speedtest.net tests hadn’t been coming close to anything I used to get, however, today I ran one just for fun and received the following:

That’s inline with what I had been receiving, so I’m glad to see those sorts of results. FiOptics continues to be fast overall, though I’m still disappointed that some major providers cannot (or will not) transmit data more than about 100 Mbps. Services like Netflix are still essentially instant. The part I’m most used to day-to-day is that we can have many devices streaming or downloading (or uploading; backups) and no single device is ever affected by any another.
For anyone that might be interested, when you take two FiOptics locations with similar speeds (my office being the other location; 500 / 125 Mbps) and connect them via a VPN tunnel, it feels as if everything is on the same local network. I have Ubiquti UniFi products installed at these two locations, so creating a VPN connection between locations is very easy. With that connection in place I can remotely control devices and have the same (lag) experience as if I were onsite. It’s an unexpected benefit that has proven very useful.
I continue to recommend this service to anyone who is OK paying the price premium — it has been a solid decision thus far.
2017-11-25 Update
Recently I’ve been testing out some new networking firmware, but ended up needing to revert to their stable codebase. Just to make sure things were working correctly, I performed a random speedtest.net test and received the following:

This is an a holiday weekend, so I’m guessing the tubes are light this afternoon (12:34 eastern), but I felt the result was pretty superb considering I have Spotify streaming, and the TV is streaming PBS in the other room.
I also realized that I’ve had gigabit service for three years now, and my only real complaint is that I assumed it would be cheaper now. At my location, I essentially have zero downtime, and I never notice any services being sluggish — though sometimes Netflix can take an extra second during the prime TV viewing hours.
FiOptics gigabit is still something I would recommend!
2018-04-24 Update

2019-11-28 Update

2020-08-09 Update

2021-12-07 Update













